Role of Diet in Lung Diseases: COPD
What are Lung Diseases
Lung diseases, such as emphysema, chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are thought to be important causes of death and indisposition worldwide. These diseases related to the lifestyle and also to some extent environmental problems. India is the one of the top most countries to be affected by COPD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) mainly remains un-diagnosed because it progresses slowly and shows the symptoms at a very late stage of progress. The prevalence of COPD varies from 3-8% among Indian males and 2.5-4.5% among Indian Females. It contributes significantly to mortality and morbidity rates in India and the world over. COPD is responsible for early mortality, high death rate and significant cost of health system. The projection for 2020 indicates that COPD will be the 3rd leading cause of death worldwide and 5th leading cause of the years lost through early mortality.
All these is a lung disease are caused by the inflammation of the respiratory system including lungs and the airway which cause obstruction of the airways, leading to difficulty in breathing, cough, wheezing and excess mucus production.
To understand the disease progress, we need to understand the anatomy of respiratory system. The respiratory system consists of the
1. Nose
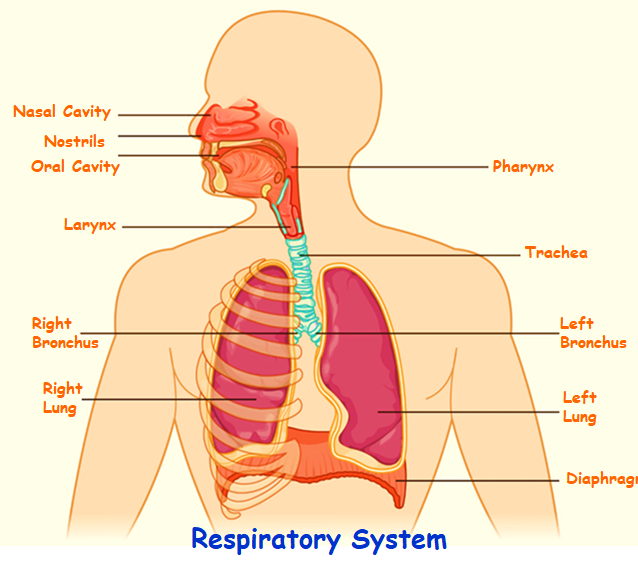
a. Nostrils
b. Nasal cavity
2. Windpipe or Trachea
a. Larynx
b. Pharynx
3. Bronchial tubes: one bronchus for each lung and
4. Lungs:
a. Bronchioles
b. Alveoli or air sacs
Chronic inflammation, either in the bronchial tubes (chronic bronchitis) or the alveoli (Emphysema), can both contribute to the development of obstructive lung disease.
The American Thoracic Society defines COPD as a disease state characterized by the presence of airflow obstruction due to chronic Bronchitis or emphysema. The air flow obstruction is generally progressive and accompanied by airway hyperactivity and may be partially reversible.
Causes:
1. Genetics: it may run in families
2. Lifestyle: diet and cigarette smoking, and
3. environmental factors: air pollution; smog, fumes and ill ventilated homes
Our main focus here is on the lifestyle factors.
Lifestyle factors like diet and smoking play an important role in the  development of this disease. Studies have shown that a diet high in calories from simple carbohydrates, high intake of cured meats, low in certain nutrients such as Vitamin C, D, E, omega-3 fatty acids and fibre, along with smoking are major causal factors of COPD. A number of researchers have found positive correlation between high fibre intake from dietary sources, such as cereals, fruits and vegetables, with improved lung function was found along with reduction in COPD related symptoms and mortality because of COPD.
development of this disease. Studies have shown that a diet high in calories from simple carbohydrates, high intake of cured meats, low in certain nutrients such as Vitamin C, D, E, omega-3 fatty acids and fibre, along with smoking are major causal factors of COPD. A number of researchers have found positive correlation between high fibre intake from dietary sources, such as cereals, fruits and vegetables, with improved lung function was found along with reduction in COPD related symptoms and mortality because of COPD.
Role of Diet:
Increased consumption of foods with simple carbohydrates have been found to increase weight, cause inflammatory changes in the lung and hypo-ventilation, that is reduction in the amount of air entering the lungs leading to various lung diseases. Examples of simple carbohydrates are table sugar, white bread, cakes, cookies, juices, chips, candy and carbonated beverages, etc. These mostly provide empty calories and do not contain disease 
 preventing nutrients, such as vitamin C,D,E or omega-3 fatty acids and are also low in fibre. Diets including more of the following foods have better physiological effects and assist in strengthening the respiratory system, thus improving the lung function.
preventing nutrients, such as vitamin C,D,E or omega-3 fatty acids and are also low in fibre. Diets including more of the following foods have better physiological effects and assist in strengthening the respiratory system, thus improving the lung function.
1. Whole grains like whole wheat, brown rice, oats. These foods are high in fibre.
2. Pulses and legume. Especially whole and with husk such as black gram, green gram whole or broken, kidney beans, soy, etc. These are also fibre rich foods and also vitamin D.
3. Vegetables: especially green leafy vegetables, beans and peas, etc. Are fibre rich and also rich in vitamin C & E.
4. Fruits: fresh fruits such as melons, oranges, papaya, etc. Fibre rich foods along with many antioxidants such as vitamin C & E.
5. Omega-3 rich foods such as walnuts and  seeds such as chia and flax, and oils like soybean oil, flax-seed oil and canola.
seeds such as chia and flax, and oils like soybean oil, flax-seed oil and canola.
The results of many studies indicated that a high intake of fibre, especially from cereals and whole grains, was inversely proportional to the development of COPD, due to its anti-oxidative and ani-inflammatory properties and that low fibre reduces overall lung function.
Apart from diet, smoking has been found to be the single major cause of reduced lung function. This could also be due to the fact that smokers generally tend to have different food habits as compared to non-smokers.
Improving physical activity level along with stress management have been found to have a positive effect on overall lung function and prevent COPD. People already suffering from COPD need to consult an expert before starting any new exercise.
So, a diet high in fibre and rich in omega-3 fatty acids along with certain vitamins C, D and E help prevent and cure the disease. Reducing or totally giving up smoking along with increased physical activity improve have been found to improve lung function.